Tokenomics is one of the most important parts of any blockchain project. Tokenomics auditing is the latest addition to this field. My seminal work in the BankX audit was really what kickstarted the whole field of auditing.
The idea behind tokenomics auditing is that you break down a project into different parts, and stress test them. I explained more about the different methods in my paper Auditing Tokenomics: A Case Study and Lessons from Auditing a Stablecoin Project.
In that paper I described the following methods:
- Empirical Proof, Data Analysis, and Benchmarking
- Agent based modelling
- Game theory
- Marginal cases analysis
- Probability theory
Me and my team had the opportunity to put this model into test for a new audit. This time it was Algem. You can read the full tokenomics audit here, but a summary is provided below.
Tokenomics audit preliminaries
Algem is a liquid staking and liquid lending solution for the Astar network. Astar is a multichain smart contract platform that connects the Polkadot ecosystem to Ethereum, Cosmos, and all major Layer 1 Blockchains.

Algem’s objective is to provide liquid staking services for Astar. On top of this, Algem incorporates a functionality called liquid lending, which takes the whole concept of liquid assets even further.
Algem has a complicated token flow. The system is using Astar vaults in order to provide yield for the end-user. At the same time, it uses its own native ALGM token for different purposes, from providing rewards to governance
Such a complicated decentralised financial infrastructure presents some unique challenges. All blockchain projects want to have a token that will appreciate, and will be stable. On top of that, DeFi projects need to ensure that they are stable, they are not ponzi-like. Algem’s liquid lending solution is also unique in its own regard, and introduced some novel mechanics which required a considerable amount of time to analyse.
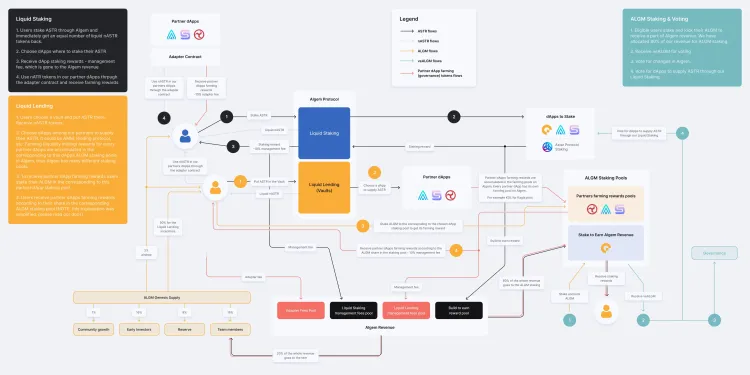
Algem tokenomics audit step 1: Structural analysis
Algem’s tokenomics audit started with what we call structural analysis. Structural analysis is a combination of techniques including game theory, and the token value flow creation.
You can see the value flow in the image below (click to enlarge).
We also analysed all demand and supply drivers and defined the balance that needs to exist in order for the token to appreciate in value. An example of such an equation is show below.
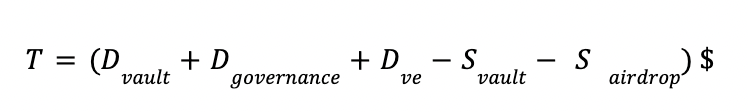
For each one of the functionalities (liquid staking and liquid lending) we identified any risks that might exist, and justified we they might or they might not take place.
Tokenomics audit step 2: Agent based modelling
The second stage of the analysis concerns agent-based modelling. You can see the results of a single run below.
One of the main challenges we encountered in simulations was the assumptions we had to make about demand pressure. All models and simulations are based on assumptions. One of the hardest things to do is to make sure that these assumptions are not too far off from reality.
One of the things we required for Algem, was to define what is called “demand pressure”, that is, how much of the token is bought at every iteration. While doing research into this, we stumbled upon a very interesting finding.
We studied different protocols, from Ethereum to Lido Finance. What we discovered is that demand pressure seems to
More specifically, let’s define demand pressure as a function of the total market cap. The demand pressure is the change in marketcap between two units of time, over the total market cap. When this quantity is negative, this indicates that demand was more than supply. Hence, we need to multiply by -1, in order to define demand pressure as a positive quantity. If it is positive, then it’s sell pressure.

Definition of demand pressure
So, what we discovered is that this quantity follows a standard normal distribution, and the standard deviation is usually between 2%-5% irrespective of the project, the size of the project, or even the period we are examining. You can see an example histogram of demand pressure shown below.
The findings of the agent based simulation helped inform the audit of the token distribution and allocation. We ensured that the token will not face unnecessary supply pressures throughout its lifetime.
Audit step 3: Improvements
In the third step, we used the results of the previous analyses, in order to propose various improvements over the original protocol. We helped develop some new mechanisms which provide additional demand drivers, and can help increase the price of the token. Also, we made sure that these new mechanisms are adaptive, and are determined through governance. This creates a virtuous cycle where:
- The mechanisms can be engaged to increase demand, when this is needed.
- In order to participate in governance, users need to buy ALGM tokens, which further increases demand.
- Governance becomes more valuable, because there are more ways for users to voice their opinion.
Tokenomics audit checklist
Algem’s tokenomics audit was also an opportunity for us to test our new tokenomics audit checklist. This is a more formalised way to test tokenomics projects. The audit checklist covers the following 4 aspects:
- Structure
- Does the system external incoming cash-flows?
- Does it contain ponzi-like elements?
- Is the system susceptible to internal shocks, or only external shocks?
- Allocation
- Does the allocation favour pump-and-dumps?
- Does it provide unnecessarily large stakes to certain actors?
- Distribution
- Does the distribution protect against pump-and-dump schemes?
- Does the distribution avoid creating unecessary sell pressure?
- Stress tests
- Does the token appreciate when simulated?
- How much external pressure (e.g. drop in demand) can the token take before it collapses?
- Does the system have feedback loops, which could accelerate a crash (e.g. the Terra/Luna case)
Blockchain, token economics, DeFi and AI
If you are interested in topics such as tokenomics, blockchain, DeFi, but also data science and AI, make sure to get in touch. I would be more than happy to speak with you. Also, please make sure to check out the page of the Tesseract Academy, my consultancy which deals with education and services in the both the areas of AI and blockchain. There is also a great framework for tokenomics which you can find on that page.
Also, make sure to check out this article on how to read ICO white papers. While ICOs have now evolved into IEOs (Initial Exchange Offerings), and IDOs (initial DEX offerings), the lessons in that article are still relevant.

