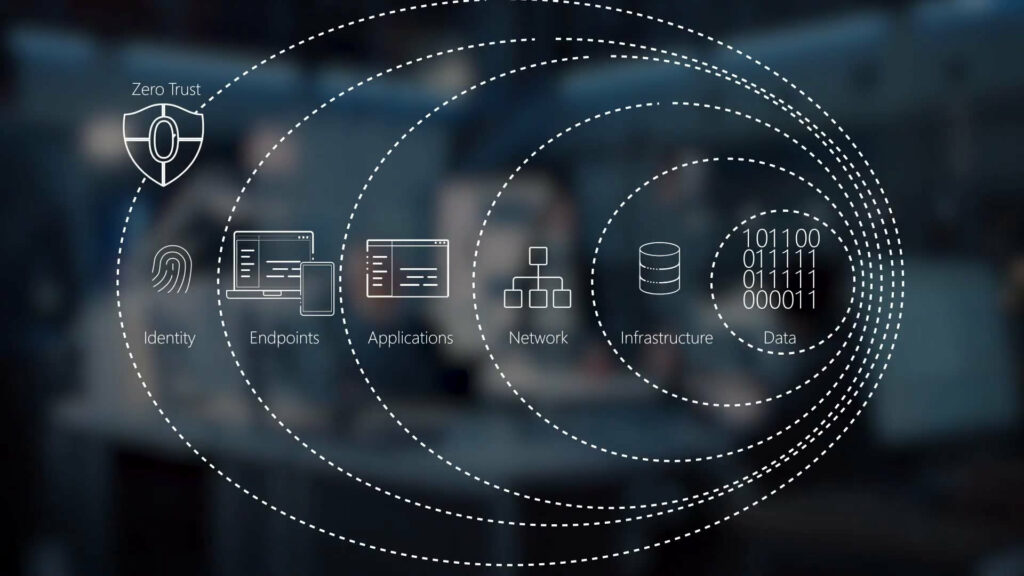
The modern digital world is not only widespread but also highly interconnected, which makes robust data security more important than ever. Traditional security models, which often rely on a fortified perimeter, are becoming less effective as the boundaries of organizational networks expand and blur. Cyber threats are also growing increasingly sophisticated and pervasive as modern hackers take advantage of contemporary technologies to bypass conventional safeguards.
These days, solutions like Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) are facilitating a pivotal paradigm shift in cybersecurity. ZTNA operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” which means that zero trust solutions vet every access to the network request regardless of origin. Another notable aspect of ZTNA’s growing appeal is its accessibility. Contrary to the assumption that advanced security frameworks are invariably costly, low-cost or even free ZTNA solutions are making headway. These security tools are pivotal for smaller businesses or those just beginning their digital transformation journey.
Because of all the marketing gimmicks out there, many are still confused on what ZTNA is. Here, let’s explore the five core principles of ZTNA in depth:

Least Privilege Access
The first cornerstone of ZTNA is the principle of Least Privilege Access. In essence, this means providing users or systems with the absolute minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks. Employees in a company’s finance department, for instance, naturally need access to its financial records, but there’s no reason for them to be able to open its human resources files. Under the Least Privilege Access model, their credentials would enable them to view only the necessary financial documents, effectively walling off unrelated or sensitive data. This targeted access minimizes the potential impact of a data breach and also makes managing user permissions simpler.
Implementing this principle can be particularly beneficial in environments where numerous users interact with diverse sets of data. By compartmentalizing access rights, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of internal and external threats.
Continuous Monitoring and Verification
In a zero-trust environment, verification is an ongoing process rather than a one-time event. ZTNA systems are constantly verifying the identity and security status of a user or device throughout its interaction with the network. This dynamic approach is akin to a security system that doesn’t just check credentials at the entrance but keeps an eye on movements within the premises, ready to respond to any unauthorized activity.
This continuous monitoring is vital for detecting and mitigating potential threats in real-time. If a user’s behavior suddenly deviates from their typical pattern—such as accessing files at odd hours or attempting to enter restricted areas—the system can immediately flag these activities and notify administrators. As modern cyber threats can emerge from seemingly benign interactions, this more proactive approach to cybersecurity can help organizations catch and neutralize them before they have the chance to do any significant damage.
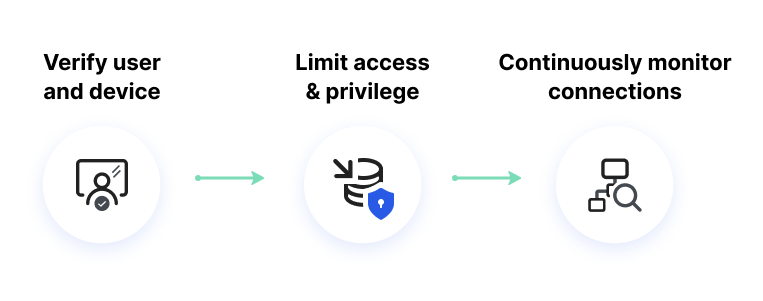
Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation takes network security a step further. Instead of having a single, monolithic security perimeter, it involves dividing the network into smaller, distinct segments. Each segment can have its own security protocols and access controls, much like having separate, secured rooms within a single building. This granular approach allows companies to control who can access specific parts of the network and what they can do within those segments.
The beauty of microsegmentation lies in its ability to limit the spread of breaches. If an intruder compromises one segment, the breach doesn’t necessarily give them access to the entire network. This compartmentalization is crucial in minimizing the impact of potential security incidents. Moreover, microsegmentation facilitates more precise security policies that are tailored to the specific needs and risks of each segment. This level of customization enhances security and supports regulatory compliance, as it ensures that sensitive data, such as financial or personal information, receives the highest level of protection.
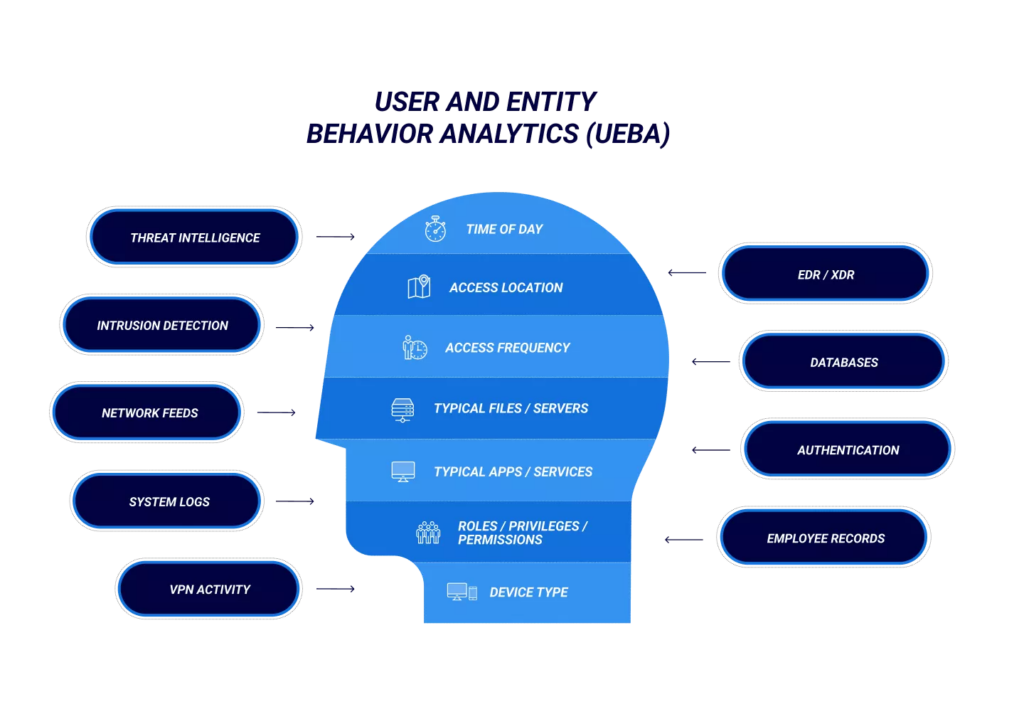
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) tools are designed to analyze and learn from the behavior of users and devices within a network. By establishing a baseline of normal activities, these tools can thus detect anomalies that may signal a security threat. For example, if a user suddenly downloads a large volume of data or accesses sensitive information they normally wouldn’t, the UEBA system would flag this as suspicious.
UEBA is particularly effective in identifying insider threats and compromised accounts, which are often hard to detect through traditional security measures. As behaviors deviate from the norm, the system alerts administrators, which in turn allows for quick investigation and decisive response.
End-to-End Encryption
The final principle, End-to-End Encryption, is vital in safeguarding data integrity and privacy. In a Zero Trust framework, data is encrypted both at rest and in transit. This means that from the moment data leaves its source to the point it reaches its destination, it remains encrypted and unintelligible to unauthorized parties who might intercept it. This is particularly crucial in highly digitalized business environments where data often traverses multiple networks and devices.
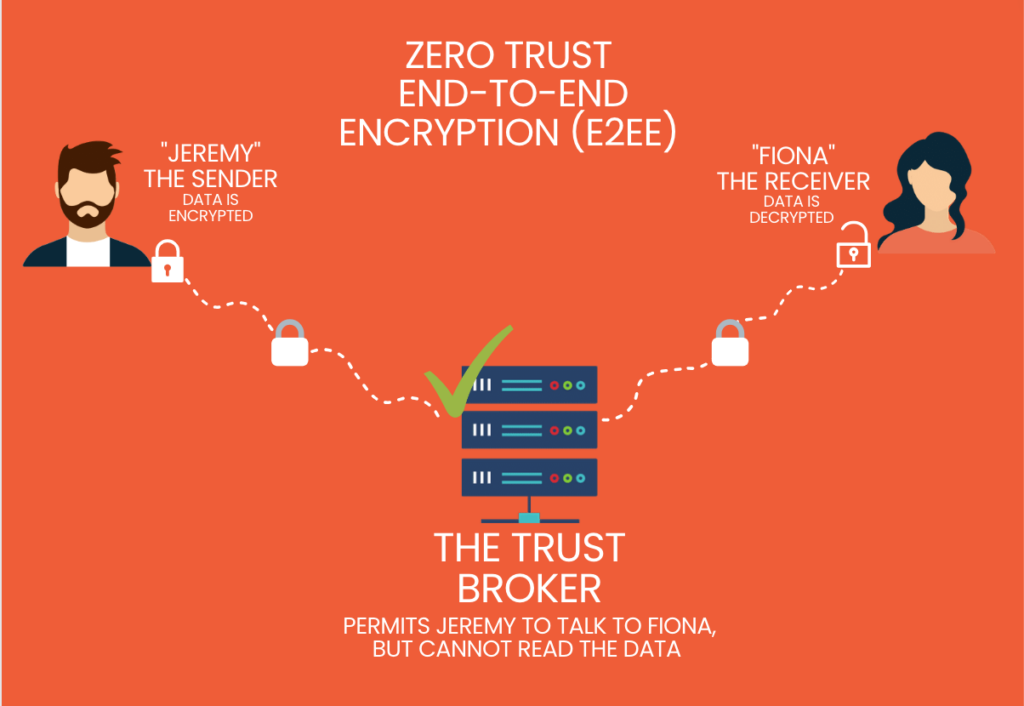
In navigating the complexities of modern cybersecurity, the principles of Zero Trust Network Access offer a robust blueprint for safeguarding digital assets. As organizations grapple with evolving threats, data security solutions become indispensable for the way they balance simplicity with efficacy in data security and compliance. Embracing these principles is thus a necessary step towards building a secure and resilient digital future for businesses of all sizes.

>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Strengthen Your Online Privacy and Infrastructure Security
Ready to take your cybersecurity to the next level?
Consider enrolling in Tesseract Academy’s GDPR, Data Privacy, and Cybersecurity course for Small Businesses. This comprehensive program equips you with essential strategies for fortifying your defense against online threats.