Artificial intelligence (AI) governance ensures the safety and ethicality of AI tools and systems by establishing regulations, guidelines, and benchmarks. Discover how AI governance shapes the future of technology and society.
What Is AI Governance?
AI governance ensures ethical AI development by addressing risks such as bias, privacy infringement, and misuse. It requires various stakeholders, including developers, users, policymakers, and ethicists, to align AI systems with societal values.
Given that AI is prone to human biases and errors, governance provides a structured approach to mitigate these risks. It involves monitoring, evaluating, and updating machine learning algorithms to prevent flawed or harmful decisions.
Responsible AI development requires addressing risks like bias, discrimination, and liability. Governance achieves this through sound policy, regulation, data governance, and well-maintained datasets. It aims to align AI behaviors with ethical standards and societal expectations while safeguarding against potential adverse impacts.
Why Is AI Governance Important?
AI governance ensures compliance, trust, and efficiency in AI development and application. The need for robust governance becomes evident as AI becomes more integrated into organizational and governmental operations. The use of AI black box systems in influencing critical decisions in criminal justice for over two decades underscores the crucial role of governance.
According to reports, US judges used the system for bail and sentencing decisions. An investigation found that the system produced false positives for black people and false negatives for white people, suggesting that black people would reoffend when they did not, and vice versa for white individuals. However, the developer of the system has disputed these findings.
AI governance provides guidelines to balance innovation with safety, upholding human dignity and rights. Transparent decision-making is essential for accountability and fairness. Additionally, governance ensures ongoing ethical standards, addressing drift in AI models and promoting responsible growth.

Core Principles of Ethical AI Governance
Adopting ethical AI governance principles is vital for organizations to safeguard themselves and their customers. The following principles guide organizations in ethically developing and deploying AI technologies:
Accountability
When working with AI, you should ensure that systems function correctly and adhere to ethical principles. Checking responsibility includes maintaining auditability, minimizing negative impacts, and reporting any issues or trade-offs that arise.
Fairness
It is essential to prioritize fairness and equity when designing AI. Companies can do this by proactively identifying and eliminating biases while promoting diversity and inclusion. The AI engineers should construct a system that does not discriminate against any individual or group based on protected characteristics like race, gender, or age.
Privacy and Security
When addressing privacy and security concerns, you should prioritize safeguarding personally identifiable information, upholding strong data ethics, and respecting fundamental human rights. You should also adhere to data owner consent to maintain trust and integrity in handling sensitive data.
Transparency
AI engineers should prioritize features like explainability, understandability, and traceability in AI system development. These elements enhance clarity, foster trust, and contribute to successful deployment and acceptance.

Implementing AI Governance
Best practices in AI governance help ensure an organization’s responsible and efficient implementation of artificial intelligence systems. Explore the five foundational principles for effective AI governance.
Data Governance and Security Measures
Enterprises often gather and use sensitive consumer data, including demographics, social media activity, geographical information, and online shopping patterns, with artificial intelligence. Companies should establish robust data security and governance standards to maintain the integrity of AI system outcomes and comply with data security and privacy laws.
Organizations can effectively mitigate the risks of data theft or exploitation by utilizing specific AI governance and security rules. This proactive approach protects sensitive consumer information and builds trust, ensuring responsible AI governance while leveraging valuable insights from consumer data.
AI Model Management
For organizations, implementing continuous monitoring, model updates, and ongoing testing is crucial to ensure the performance of AI models. With time, AI models may degrade, resulting in undesirable outcomes.
Regular testing enables detecting and resolving issues like model drift, ensuring system reliability. Furthermore, periodic model refreshes help incorporate new data and insights, improving accuracy and relevance. Continuous monitoring facilitates real-time assessment, allowing prompt interventions to maintain the system’s intended functionality.
Framework Implementation Strategies
Organizations should implement robust AI governance frameworks to ensure compliance. The framework should establish a reporting structure for senior leadership. Fostering an AI ethics-focused culture, effectively communicating findings, conducting regular audits, and defining clear roles and ownership for managing AI systems.
Creating a reporting mechanism reaching senior leadership ensures liability and prompt action. Educating staff on AI ethics promotes awareness and responsible practices. Routine audits identify potential issues and ensure compliance, while clear role definitions streamline decision-making.
These measures strengthen AI governance frameworks and promote ethical AI practices throughout the organization.
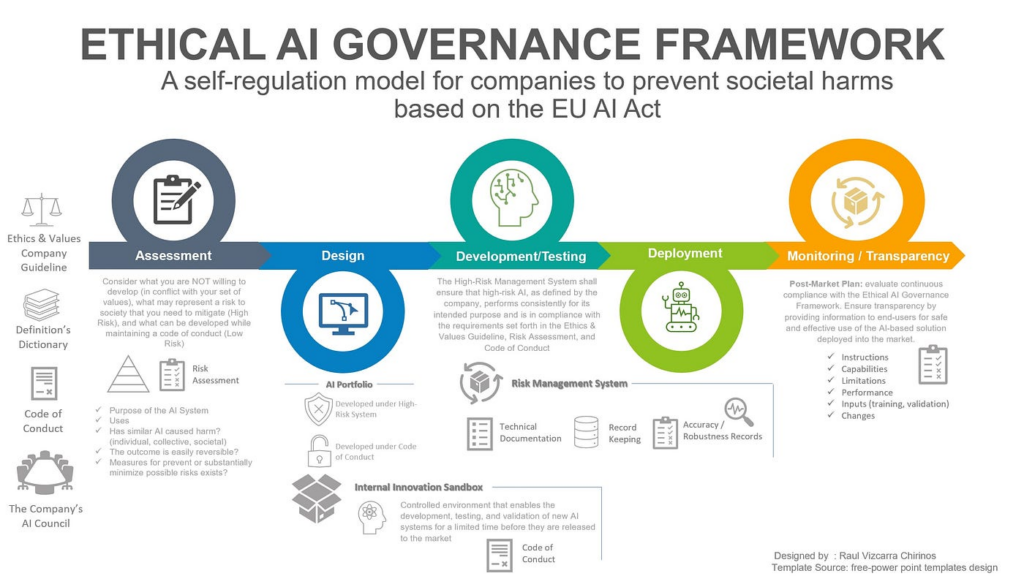
image source
Algorithmic Bias Remediation
Utilizing various algorithms will address unintentional biases in AI systems. These biases, stemming from human cognitive tendencies, can result in unfairness, impacting areas like hiring and customer service based on gender or race.
Techniques such as option-based categorization and adversarial debiasing help identify and correct biases. Tools like what-if analysis enable interactive examination, stress testing, and identification of limitations, promoting fairness and equity in AI systems and thereby preventing unjust discrimination.
Enhancing Explainability and Transparency
Developers often prioritize accuracy over improving model clarity, overlooking its crucial importance. Initially, AI systems were treated as opaque “black boxes,” revealing little about their inner workings beyond input and output.
However, growing concerns about accountability in automated decision-making have led to regulatory measures like GDPR, which mandates explanations. Resolving conflicts stemming from AI solutions requires understanding their inner workings to assign responsibility accurately.
Several methods, such as proxy modeling with decision trees and the “interpretability by design” approach, help us understand complex models better. Organizations should foster trustworthy AI systems by emphasizing model transparency alongside accuracy.
Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
Developing a robust AI governance framework involves management, personnel, customers, partners, information security experts, and regulators. This inclusive approach incorporates diverse perspectives and expertise to address several issues.
Engaging stakeholders throughout the process promotes accessibility, openness, and a shared understanding of ethical and practical considerations in AI systems.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Organizations must establish procedures for ongoing monitoring and auditing of AI systems to uphold ethical standards. They can do this by regularly evaluating data sources, assessing model behavior, and tracking performance metrics.
Continuous monitoring helps detect and address biases, data drift, or system degradation. Regular audits verify compliance with regulations, identify areas for improvement, and ensure the AI systems function correctly. By implementing these practices, organizations can uphold their AI systems’ integrity, fairness, and effectiveness.
Conclusion
AI governance is crucial for the responsible development and deployment of artificial intelligence. Adhering to principles like accountability, fairness, privacy, security, and clarity helps mitigate risks of bias and discrimination. Prioritizing ethics in AI is essential for innovation while safeguarding against harm, shaping a future where technology serves humanity’s interests.